Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Amamiya, Hiroki*
Dai-31-Kai Shakai Chishitsugaku Shimpojiumu Rombunshu, p.19 - 22, 2021/11
A three-year monitoring of  Cs outflow associated with soil erosion from decontaminated and burnt sites using an experimental plot was conducted in a mountainous forest of Fukushima, Japan. Corresponding with recovery of the forest floor cover, such as undergrowth and litter layer, the
Cs outflow associated with soil erosion from decontaminated and burnt sites using an experimental plot was conducted in a mountainous forest of Fukushima, Japan. Corresponding with recovery of the forest floor cover, such as undergrowth and litter layer, the  Cs outflow during the monitoring period in the rainy season of Fukushima decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% and 2.79% to 0.03% in the decontaminated and burnt sites, respectively. The forest floor cover ratio of 60% or more is a threshold for an effect on the
Cs outflow during the monitoring period in the rainy season of Fukushima decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% and 2.79% to 0.03% in the decontaminated and burnt sites, respectively. The forest floor cover ratio of 60% or more is a threshold for an effect on the  Cs outflow in the monitoring sites. In the burnt site, a change of dominant outflowed materials from soil particles into litter and its fragments also contributes to the decreasing in the
Cs outflow in the monitoring sites. In the burnt site, a change of dominant outflowed materials from soil particles into litter and its fragments also contributes to the decreasing in the  Cs outflow. A protective function of forest floor cover against the soil erosion inherent in the natural forest environment is effective for the migration control of the
Cs outflow. A protective function of forest floor cover against the soil erosion inherent in the natural forest environment is effective for the migration control of the  Cs outflow.
Cs outflow.
Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Takeuchi, Erina; Nishimura, Shusaku; Muto, Kotomi*; Matsunaga, Takeshi*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 238-239, p.106725_1 - 106725_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.09(Environmental Sciences)To understand the spatial variation in soil  Cs inventory in complex mountainous topography, a whole-area investigation of
Cs inventory in complex mountainous topography, a whole-area investigation of  Cs deposition in a broad-leaved forest catchment of a mountain stream was conducted using grid sampling. Across the catchment, organic and surface mineral soil layers were collected at 42 locations in 2013 and 6 locations in 2015.
Cs deposition in a broad-leaved forest catchment of a mountain stream was conducted using grid sampling. Across the catchment, organic and surface mineral soil layers were collected at 42 locations in 2013 and 6 locations in 2015.  Cs deposition on the forest floor exhibited high spatial heterogeneity and altitude-dependent distribution over the catchment. The
Cs deposition on the forest floor exhibited high spatial heterogeneity and altitude-dependent distribution over the catchment. The  Cs retention ratio in the organic layer ranged from 6% to 82% in 2013. The
Cs retention ratio in the organic layer ranged from 6% to 82% in 2013. The  Cs retention ratios had positive correlations with the material inventory in the organic layer and the elevation. The
Cs retention ratios had positive correlations with the material inventory in the organic layer and the elevation. The  Cs retention ratios in the organic layer were less than 20% in 2015, even at the locations where the retention ratio was higher than 55% in 2013. Although there was spatial variation in the migration speed,
Cs retention ratios in the organic layer were less than 20% in 2015, even at the locations where the retention ratio was higher than 55% in 2013. Although there was spatial variation in the migration speed,  Cs migration from the organic layer to mineral soil was almost completed within 4 y of the deposition.
Cs migration from the organic layer to mineral soil was almost completed within 4 y of the deposition.
Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tanaka, Taku*; Komatsu, Masabumi*; Gonze, M.-A.*; Sakashita, Wataru*; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Nishina, Kazuya*; Ota, Masakazu; Ohashi, Shinta*; Calmon, P.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 238-239, p.106721_1 - 106721_10, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.59(Environmental Sciences)This study was aimed at analysing performance of models for radiocesium migration mainly in evergreen coniferous forest in Fukushima, by inter-comparison between models of several research teams. The exercise included two scenarios of countermeasures against the contamination, namely removal of soil surface litter and forest renewal, and a specific konara oak forest scenario in addition to the evergreen forest scenario. All the models reproduced trend of time evolution of radiocesium inventories and concentrations in each of the components in forest such as leaf and organic soil layer. However, the variations between models enlarged in long-term predictions over 50 years after the fallout, meaning continuous field monitoring and model verification/validation is necessary.
Kim, M.; Malins, A.; Machida, Masahiko; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Saito, Kimiaki; Yoshida, Hiroko*; Yanagi, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*
RIST News, (67), p.3 - 15, 2021/09
no abstracts in English
 Cs outflow from forest floor adjacent to a residential area; Comparison of decontaminated and non-decontaminated forest floor
Cs outflow from forest floor adjacent to a residential area; Comparison of decontaminated and non-decontaminated forest floorNiizato, Tadafumi; Watanabe, Takayoshi
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 24(2), p.129 - 136, 2021/06
The 3-years monitoring of  Cs outflow associated with soil erosion in the decontaminated and no decontaminated sites using experimental plot was conducted in the forest of Fukushima during the rainy season. The
Cs outflow associated with soil erosion in the decontaminated and no decontaminated sites using experimental plot was conducted in the forest of Fukushima during the rainy season. The  Cs outflow in the decontaminated site was 10 to 14 times larger than that of no decontaminated site. However, the outflow in the decontaminated site decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% in corresponding with the recovery of the forest floor cover. When reaching of the forest floor cover to 60% and over, the
Cs outflow in the decontaminated site was 10 to 14 times larger than that of no decontaminated site. However, the outflow in the decontaminated site decreased from 3.24% to 0.61% in corresponding with the recovery of the forest floor cover. When reaching of the forest floor cover to 60% and over, the  Cs outflow in the decontaminated site turned into relatively minor fluctuations and similar level to the no decontaminated site. The decrease in the
Cs outflow in the decontaminated site turned into relatively minor fluctuations and similar level to the no decontaminated site. The decrease in the  Cs outflow corresponding to the restoration of the forest floor cover was owing to the recovering of the protective effect of forest floor against the raindrop splash and decrease in ratio of the soil component with relatively high
Cs outflow corresponding to the restoration of the forest floor cover was owing to the recovering of the protective effect of forest floor against the raindrop splash and decrease in ratio of the soil component with relatively high  Cs activity in the particulate matter.
Cs activity in the particulate matter.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Kanasashi, Tsutomu*; Takenaka, Chisato*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Science of the Total Environment, 755(Part 2), p.142598_1 - 142598_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.21(Environmental Sciences)In this study, we investigated coordination structures of Cs in  Cs-doped bark, sapwood, heartwood, needle, and branch samples of trees collected in Fukushima by extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. We examined four representative tree species in Fukushima,
Cs-doped bark, sapwood, heartwood, needle, and branch samples of trees collected in Fukushima by extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. We examined four representative tree species in Fukushima, 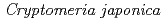 ,
, 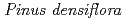 ,
, 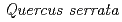 , and
, and 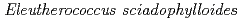 . EXAFS spectra suggested that Cs was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on all parts of the four species, with electrostatic binding to negatively charged functional groups in components of tree tissues. These results were supported by extraction experiments where most of the sorbed Cs was desorbed from all parts of each tree species using 1 M CH
. EXAFS spectra suggested that Cs was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on all parts of the four species, with electrostatic binding to negatively charged functional groups in components of tree tissues. These results were supported by extraction experiments where most of the sorbed Cs was desorbed from all parts of each tree species using 1 M CH COONH
COONH .
.
 Cs and
Cs and  Cs radioactivity measurements
Cs radioactivity measurementsMalins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Takahashi, Junko*; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 226, p.106456_1 - 106456_12, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.21(Environmental Sciences)Kurikami, Hiroshi
Impacts of Fukushima Nuclear Accident on Freshwater Environments, p.227 - 247, 2021/00
The relationship between radiocesium migration in forest and fish contamination was analyzed by using a model and environmental monitoring data. As the result, it was estimated that radiocesium sources in forest transferred to fish were changing with time. In the first several years after the accident, the main sources were leaves that fell directly into rivers and litter layer of the forest floor, which led the fast decrease of radiocesium concentration in fish. After the period, the main source was switched to the organic soil underlying the litter layer.
 Cs in organic layer and mineral soil in Japanese forests; Four-year observation and model analysis
Cs in organic layer and mineral soil in Japanese forests; Four-year observation and model analysisMuto, Kotomi; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Matsunaga, Takeshi*; Koarashi, Jun
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 208-209, p.106040_1 - 106040_10, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.32(Environmental Sciences)Vertical distributions of  Cs in the soil profile were observed at five forest sites with different vegetation types for 4.4 years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, and
Cs in the soil profile were observed at five forest sites with different vegetation types for 4.4 years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, and  Cs migration in the organic layer and mineral soil was analyzed based on a comparison of models and observations. Cesium-137 migration from the organic layer was faster than that observed in European forests, suggesting that the mobility and bioavailability of
Cs migration in the organic layer and mineral soil was analyzed based on a comparison of models and observations. Cesium-137 migration from the organic layer was faster than that observed in European forests, suggesting that the mobility and bioavailability of  Cs could be suppressed rapidly in Japanese forests. The diffusion coefficients of
Cs could be suppressed rapidly in Japanese forests. The diffusion coefficients of  Cs in the mineral soil were estimated to be 0.042-0.55 cm
Cs in the mineral soil were estimated to be 0.042-0.55 cm y
y , which were roughly comparable with those of European forest soils affected by the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant accident. Model predictions indicated
, which were roughly comparable with those of European forest soils affected by the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant accident. Model predictions indicated  Cs mainly distributed in the surface mineral soil at 10 years after the accident. It suggest that the
Cs mainly distributed in the surface mineral soil at 10 years after the accident. It suggest that the  Cs deposited onto Japanese forest ecosystems will be retained in the surface layers of mineral soil for a long time.
Cs deposited onto Japanese forest ecosystems will be retained in the surface layers of mineral soil for a long time.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Namba, Kenji*; Neda, Hitoshi*; Sasaki, Yoshito; Niizato, Tadafumi; Watanabe, Naoko*; Kozaki, Tamotsu*
Environmental Science; Processes & Impacts, 21(7), p.1164 - 1173, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:44.69(Chemistry, Analytical)The fate of radioactive Cs deposited after the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident and its associated radiological impacts are largely dependent on its mobility from surface soils to forest ecosystems. We measured the accumulation of radioactive Cs in the fruit bodies of wild fungi in the forest at Iidate, Fukushima, Japan. The transfer factors (TFs) of radioactive Cs from soil to the fruit bodies of wild fungi were between 10  to 10
to 10 , a range similar to those reported for the fruit bodies collected in Europe after the Chernobyl accident and in parts of Japan contaminated by nuclear bomb test fallout. Comparison of the TFs of the wild mushroom and that of the fungal hyphae of 704 stock strains grown on agar medium containing nutrients and radioactive Cs showed that the TFs of wild mushroom were lower. TF was less than 0.1 after addition of the minerals zeolite, vermiculite, phlogopite, smectite, or illite of 1% weight to the agar medium. These results indicate that the presence of minerals decrease Cs uptake by fungi grown in the agar medium.
, a range similar to those reported for the fruit bodies collected in Europe after the Chernobyl accident and in parts of Japan contaminated by nuclear bomb test fallout. Comparison of the TFs of the wild mushroom and that of the fungal hyphae of 704 stock strains grown on agar medium containing nutrients and radioactive Cs showed that the TFs of wild mushroom were lower. TF was less than 0.1 after addition of the minerals zeolite, vermiculite, phlogopite, smectite, or illite of 1% weight to the agar medium. These results indicate that the presence of minerals decrease Cs uptake by fungi grown in the agar medium.
Okano, Yasushi; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2017/11
Forest fire hazard assessment methodologies using a logic tree have been applied for the evaluation of combination hazard curves of a forest fire with lightning as an initiator of a forest fire and with a strong wind being independent from a forest fire. The complex shape of the combinational hazard curve of forest fire and lighting is due to that both lightning and high velocity wind tend to appear under unstable weather conditions, and there is correlation between two hazards. The evaluated combinational hazard curve of forest fire and strong wind for the instantaneous wind velocity over 80 m/s has extremely small frequency in the range below 10 /year.
/year.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Dohi, Terumi; Nakama, Shigeo; Funaki, Hironori; Misono, Toshiharu; Oyama, Takuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Seiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-018, 86 Pages, 2017/10
Since the accidents at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant following the Tohoku Region Pacific Coast Earthquake on March 11th, 2011, Fukushima Environmental Safety Center has carried out research on natural mobilization of radionuclide (especially radiocesium) and future forecast from forest to water system and surrounding residential areas. The report summarizes the latest results that have been accumulated from each study field, of our agency together with the other related research organizations. The contents of the report is to be used as evidence-based information for the QA-styled pages in the website of JAEA Sector of Fukushima Research and Development at the time of next renewal.
Hemmi, Ko; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 24(1), p.3 - 14, 2017/06
Conditions of contaminated sources and ranges of forest decontamination that significantly reduce the air dose rate in residential areas were investigated by means of a sensitivity analysis related to the decontamination of the forest contaminated by radiocesium deriving from the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The contaminated sources including  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were assumed to be a layer of sedimented organic matter (the A
Cs were assumed to be a layer of sedimented organic matter (the A layer) and surface soils (the A
layer) and surface soils (the A layer). The air dose rates were calculated using the three-dimensional Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. A slope number of the forest, angles, state of contaminant distribution, radiocesium content in the forest soils, decontamination ranges, distance from the forest boundary to an evaluation point, and height at the evaluation point were adopted as the parameters. The decontamination of a litter (A
layer). The air dose rates were calculated using the three-dimensional Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. A slope number of the forest, angles, state of contaminant distribution, radiocesium content in the forest soils, decontamination ranges, distance from the forest boundary to an evaluation point, and height at the evaluation point were adopted as the parameters. The decontamination of a litter (A ) layer within the distance of 20 m from the forest boundary was revealed to be effective in reducing the air dose rate when the source distribution was homogeneous. The air dose rates were significantly reduced by the decontamination of the A
) layer within the distance of 20 m from the forest boundary was revealed to be effective in reducing the air dose rate when the source distribution was homogeneous. The air dose rates were significantly reduced by the decontamination of the A layer within a distance of 40 m from the forest boundary on condition that the radiocesium content of the A
layer within a distance of 40 m from the forest boundary on condition that the radiocesium content of the A layer was larger than that of the A
layer was larger than that of the A layer and the source distribution was non-homogeneous, such as the forest areas beyond 20 m from the forest boundary, which were more heavily contaminated than those within 20 m.
layer and the source distribution was non-homogeneous, such as the forest areas beyond 20 m from the forest boundary, which were more heavily contaminated than those within 20 m.
Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Mitachi, Katsuaki; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ishii, Yasuo; Watanabe, Takayoshi
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 161, p.11 - 21, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:67.86(Environmental Sciences)Estimations of radiocesium input and output budgets concerning the forest floor in a mountain forest region have been conducted in the north and central part of the Abukuma Mountains of Fukushima, after 2 to 3 year period following the TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The radiocesium input and output associated with surface washoff, throughfall, stemflow, and litterfall processes at the experimental plots have been monitored on a forest floor of evergreen Japanese cedar and deciduous Konara oak forests. The results at both monitoring locations show the radiocesium input to be 4-50 times higher than the output during the rainy season in Fukushima. These results indicate that the radiocesium tend to be preserved in the forest ecosystem due to extremely low output ratios. Thus, the associated fluxes throughout the circulation process are key issues for the projecting the environmental fate of the radiocesium levels.
Shimomura, Yusuke; Hanari, Akira*; Sato, Isamu*; Kitamura, Ryoichi
JAEA-Technology 2015-062, 47 Pages, 2016/03
In response to new standards for regulating waste management facilities, it was carried out impact assessment of forest fires on the waste management facilities existed in Oarai Research and Development Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. At first, a fire spread scenario of forest fires was assumed. The intensity of forest fires was evaluated from field surveys, forest fire evaluation models and so on. As models of forest fire intensity evaluation, Rothermel Model and Canadian Forest Fire Behavior Prediction (FBP) System were used. Impact assessment of radiant heat to the facilities was carried out, and temperature change of outer walls for the assumed forest fires was estimated. The outer wall temperature of facilities was estimated around 160 C at the maximum, it was revealed that it doesn't reach allowable temperature limit. Consequently, it doesn't influence the strength of concrete. In addition, a probability of fire breach was estimated to be about 20%. This report illustrates an example of evaluation of forest fires for the new regulatory standards through impact assessment of the forest fires on the waste management facilities.
C at the maximum, it was revealed that it doesn't reach allowable temperature limit. Consequently, it doesn't influence the strength of concrete. In addition, a probability of fire breach was estimated to be about 20%. This report illustrates an example of evaluation of forest fires for the new regulatory standards through impact assessment of the forest fires on the waste management facilities.
Iijima, Kazuki
Chikyu Kagaku, 49(4), p.203 - 215, 2015/09
The Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident led to the release of various and huge amount of radionuclides into the environment, and contamination of wide area of eastern Japan, mainly Fukushima prefecture. More than 70% of radioactive cesium, which dominates the exposure dose, was deposited in forest far from our living sphere and is considered to be remobilized with time by water flow and strong wind caused by natural events such as typhoons. Numerous researches on the behavior of radionuclides in the environment have been performed not only by observation in the contaminated regions but also by model analysis so far. This paper overviewed results of understanding and modeling of transport behavior of radiocesium from forests through river systems.
Okano, Yasushi; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Topical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Analysis (PSA 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.22 - 31, 2015/04
An external hazard curve of a forest fire is evaluated based on a logic tree. The logic tree consists domains of "forest fire breakout and spread conditions", "weather condition" and "vegetation and topographical conditions". A location nearby a typical nuclear power plant site in Japan was selected, and the frequency of a large forest fire of the location is approximately 1/5 of the average in Japan. Forest fire breakout points were selected considering typical forest fire causes in Japan. The weather conditions are represented by two parameter sets of "temperature-humidity" and "wind direction-wind speed". A number of forest fire simulations were performed to obtain a response surface for a frontal fireline intensity. The hazard curve is therefore evaluated by a Monte Carlo simulation such that the annual exceedance probability is about 1.0 10
10 per year for the frontal fireline intensity of 200 kW/m and about 1.3
per year for the frontal fireline intensity of 200 kW/m and about 1.3 10
10 per year for 300 kW/m.
per year for 300 kW/m.
 CO
CO flux at soil-atmosphere interface and distribution of
flux at soil-atmosphere interface and distribution of  C in forest ecosystem
C in forest ecosystemKoarashi, Jun; Amano, Hikaru; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Iida, Takao*; Moriizumi, Jun*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 60(3), p.249 - 261, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:34.2(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Koide, Kaoru; Yanagizawa, Koichi
PNC TN7410 93-016, 42 Pages, 1993/10
The purpose of this study is to develop estimation methods of hydrological characteristics of subsurface using regional data such as remote sensing data and topographical data in order to evaluate regional groundwater flow in Japan. This study consists of following three steps. The first step is to develop methods to extract the ground surface information. The second step is to quantify the relationship between the ground surface conditions and hydrological characteristics. And the final step is to develop estimation methods of hydrological characteristics of subsurface by using ground surface information. This paper describes the development of extraction methods on the ground surface information as the first step in our study. In this paper, topography and vegetation parameters were selected as the ground surface information which is considered relating to water balance which is one of hydrological characteristics. The study site was selected in the area (5km  5km) around the Tono uranium Mine, Central Japan. In order to extract topographic information, we developed a computer program to calculate direction and inclination of hill slopes using digital elevation map (DEM). The program was validated by comparing calculated results with measured slope data which were read from topographic map in the study site. We also examined grid intervals of DEM so that terrain in the study site can be represented appropriately. As a result, it was known that the grid interval of DEM should be less than 30m in the study site. We tried to classify forest types into three classes, a broad-leaved forest, conifer forest and mixed forest, using seasonal change of the normalized vegetation index (NVI) that was calculated from SPOT HRV data. Multi-temporal data (summer, autumn and winter) of SPOT were used to determine seasonal change of NVI of each forest type. As a result, it was definitely shown that each forest type has a different seasonal change of NVI. We ...
5km) around the Tono uranium Mine, Central Japan. In order to extract topographic information, we developed a computer program to calculate direction and inclination of hill slopes using digital elevation map (DEM). The program was validated by comparing calculated results with measured slope data which were read from topographic map in the study site. We also examined grid intervals of DEM so that terrain in the study site can be represented appropriately. As a result, it was known that the grid interval of DEM should be less than 30m in the study site. We tried to classify forest types into three classes, a broad-leaved forest, conifer forest and mixed forest, using seasonal change of the normalized vegetation index (NVI) that was calculated from SPOT HRV data. Multi-temporal data (summer, autumn and winter) of SPOT were used to determine seasonal change of NVI of each forest type. As a result, it was definitely shown that each forest type has a different seasonal change of NVI. We ...
Amano, Hikaru
Proc. of the 5th Int. Seminar for Liquid Scintillation Analysis, p.55 - 76, 1993/00
no abstracts in English